When you think of an allergic reaction, you might picture someone breaking out in a rash or their skin turning red. Hives and flushing are two of the most common signs of this. These skin symptoms usually disappear once the allergy is treated. However, there are other types of skin rashes that hang around for weeks or longer and are linked to allergies. The most common of these rashes are chronic hives, which keep coming back; eczema, an inflammatory skin condition that causes dryness and itching; and contact dermatitis, which is an eczema-like reaction that develops when your skin reacts to something it touches.
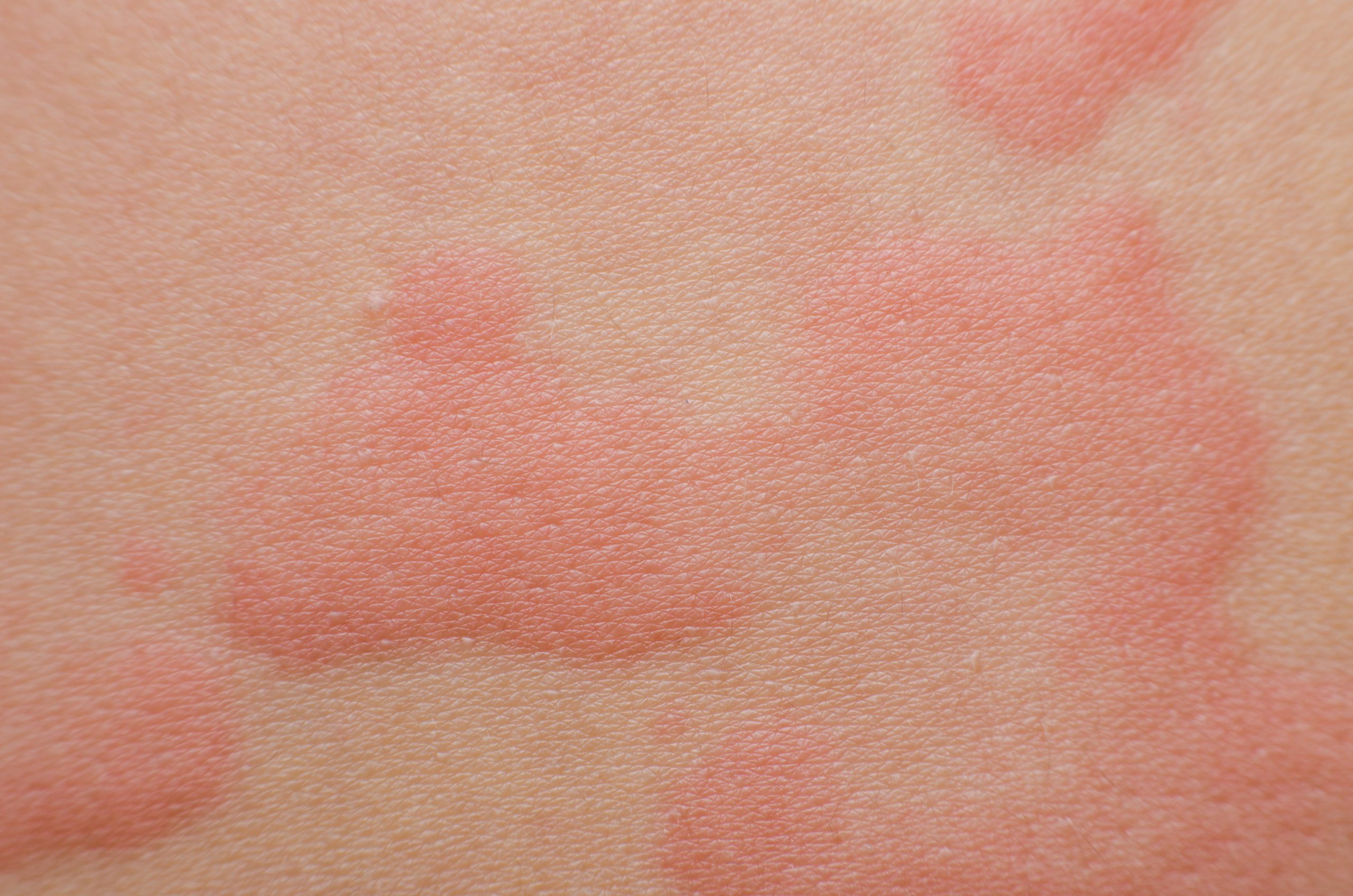
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) is a condition where you get hives (red, itchy bumps) on your skin that last for more than six weeks. Hives can appear on any area of the body. They may change shape, move around, disappear and reappear over short periods of time. The bumps – red or skin-colored “wheals” with clear edges – usually appear suddenly and go away just as quickly. “Idiopathic” means we don’t know exactly what causes it. Often, CIU is accompanied by angioedema, which is tissue swelling that often affects the face, lips, tongue, throat, hands, or feet.
In CIU and angioedema, your immune system releases a chemical called histamine. Normally, histamine helps your body fight infections, but in these conditions, it causes hives and swelling without any infection.
While CIU and angioedema can be frustrating, there are treatments that can help:
In addition to prescribing treatments, your Ohio ENT & Allergy provider may talk to you about ways to manage hives through lifestyle measures. These include:
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often appears in childhood but affects many adults as well. Managing atopic dermatitis involves understanding triggers, maintaining a skincare routine, and knowing how to identify and manage flare-ups.
Your Ohio ENT & Allergy provider can discuss ways to control your eczema through lifestyle changes. These include:
Your provider may also prescribe medication to help you manage atopic dermatitis, especially when it is severe. The number of available medications for atopic dermatitis is increasing, and includes things like:
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when your skin encounters something that causes either direct irritation or an allergic reaction. Imagine it as your skin’s way of saying, “I don’t like this!” It can happen to anyone and is often caused by everyday items like soaps, cosmetics, plants, or jewelry.
There are two main types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis is more common and happens when a substance physically damages the skin. This could be from harsh chemicals or even frequent handwashing. The other kind, allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your immune system reacts to a substance, such as nickel in jewelry or poison ivy.
The symptoms of contact dermatitis include redness, itching, swelling, or blisters on the affected area of your skin. The rash can be tough to distinguish from eczema. These symptoms usually take a few days to develop after the skin is exposed to the provoking substance.
The good news is that contact dermatitis usually clears up once you identify and avoid the offending substance. Your Ohio ENT & Allergy provider can work with you to identify contact allergens through a type of allergy test called a patch test. Once you know you’re sensitive to certain substances, your provider will guide you on how to avoid them.
In the meantime, there are ways to help soothe the irritation, such as applying moisturizing creams, using anti-itch lotions, or taking antihistamines. In severe cases, you might by prescribed an anti-inflammatory treatment.
